
Companies prefer the cloud more than on-premise data centers, also known as servers, due to the cost-effectiveness and services of the cloud. Today, 76% of enterprises use two or more cloud providers, while 35% of organizations have more than 50% of their workloads in the cloud (hybrid environment). However, moving your applications from on-prem networks to the cloud doesn’t mean they will be secure. In fact, “27% of organizations have experienced a security incident in the cloud infrastructure within the last 12 months”.
Cloud workloads also demand security. Protecting large organizations that have thousands of virtual machines running on Azure infrastructure as a service becomes a very tedious task. Microsoft, being one of the top cybersecurity vendors, has invested in building secure solutions for companies. In this article, we will talk about Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture (MCRA), the approach used to build this architecture, and its implementations.
What is Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture (MCRA)?
Microsoft Cyber Security Reference Architecture provides a clear roadmap about its security capabilities and describes the way Microsoft integrates security capabilities with its platforms, such as Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365, etc., third-party apps, including salesforce and ServiceNow, and third-party platforms, such as AWS and Google Cloud Platform.
Basically, MCRA is based on detailed technical diagrams that describe Microsoft security capabilities, people, zero trust user access, Azure Native controls, attack chain coverage, etc. Also, the reference architecture comprises an overview of the Zero Trust model and Zero Trust rapid modernization plan (RaMP), in addition to information about security operations and key initiatives, including protection from human-operated ransomware, beyond VPN usage, and more.
Introduction
Companies prefer the cloud more than on-premise data centers, also known as servers, due to the cost-effectiveness and services of the cloud. Today, 76% of enterprises use two or more cloud providers, while 35% of organizations have more than 50% of their workloads in the cloud (hybrid environment). However, moving your applications from on-prem networks to the cloud doesn’t mean they will be secure. In fact, “27% of organizations have experienced a security incident in the cloud infrastructure within the last 12 months”.
Cloud workloads also demand security. Protecting large organizations that have thousands of virtual machines running on Azure infrastructure as a service becomes a very tedious task. Microsoft, being one of the top cybersecurity vendors, has invested in building secure solutions for companies. In this article, we will talk about Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture (MCRA), the approach used to build this architecture, and its implementations.
What is Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture (MCRA)?
Microsoft Cyber Security Reference Architecture provides a clear roadmap about its security capabilities and describes the way Microsoft integrates security capabilities with its platforms, such as Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365, etc., third-party apps, including salesforce and ServiceNow, and third-party platforms, such as AWS and Google Cloud Platform.
Basically, MCRA is based on detailed technical diagrams that describe Microsoft security capabilities, people, zero trust user access, Azure Native controls, attack chain coverage, etc. Also, the reference architecture comprises an overview of the Zero Trust model and Zero Trust rapid modernization plan (RaMP), in addition to information about security operations and key initiatives, including protection from human-operated ransomware, beyond VPN usage, and more.
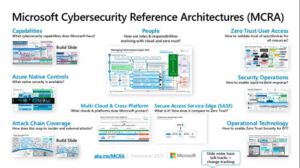
Image source: Microsoft
What is the approach behind MCRA?
Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture uses a data-centric and asset-centric approach. The purpose behind this approach is to focus on security resources and monitor assets to respond to threats, in addition to adaptive identity that enables them to respond to rapidly evolving roles, environment, responsibilities, and relationships.
Most importantly, MCRA is based on the Zero trust principles. Microsoft Zero Trust Principles include:
- Explicit verification: The zero trust model requires you to regularly validate users and all available data, including user identity, location, device health, data classification, anomalies, and service or workload context.
- The least privilege access requires limited user access to secure data and enhance productivity. This can be done using risk-based adaptive policies, just-enough-access (JEA), and just-in-time (JIT).
- Breach assumption: Stay prepared for breaches and prevent lateral movement using end-to-end encryption and analytics to detect threats and improve defenses, and segment networks, users, and devices.
Moreover, MCRA revolves around people, processes, and technology. The main aim is to enhance security around these.
- People: While people are the most important assets in any organization, they can also become a liability to the system. MCRA focuses on the roles and responsibilities evolving with cloud and zero trust. With a shift into the cloud, mindset and approach to security also need to be changed. It is necessary to educate teams about the cloud security journey and technology. Also, MCRA uses the security rapid modernization plan (RaMP) to adopt a privileged access strategy.
- Processes: The next approach is to secure processes and assign accountability for cloud security decisions to speed up the cloud adoption and secure the enterprise Azure environment. Furthermore, planning for crisis control during a crisis is not a healthy approach to defend against cloud attacks. Regularly update incident response processes for cloud security and establish security posture management to monitor security posture and mitigate risks to assets.
- Technology: The final approach is to secure technology i.e. systems, networks, and the cloud. For this, you can use passwordless login or multi-factor authentications to protect technology. Also, firewalls and network security are critical to protecting systems and data against network attacks.
How can you use MCRA?
So, basically, MCRA is not a technology or tool to implement but a security architecture or framework you can use as a reference to enhance security capabilities around the cloud, or you can adapt it according to your processes and cybersecurity posture. Organizations use Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture for different purposes. Some of them are stated below:
As a security reference architecture template
Many organizations use MCRA as a starting template to build their own security architecture. It helps them define and document expected state to enhance their cybersecurity capabilities. This reference architecture is useful for organizations as it covers security capabilities and policies around modern enterprise that spans mobile devices, on-premise data centers, clouds, and IoT devices.
Comparison with ongoing security capabilities
Several organizations use MCRA as a comparison reference for their security capabilities to identify where they stand in the evolving security environment. For this purpose, organizations can document the existing security capabilities they are already using from the Microsoft license suite and the new ones they might need in the future.
Learning Microsoft Capabilities
Organizations may also use the template to learn more about the security capabilities of Microsoft. The presentation mode of the template contains a “ScreenTip” for each capability with a short description, in addition to a link to learn more about that capability. You can learn about Microsoft’s security capabilities by following the link.
Learn about cybersecurity
MCRA provides many details about how Microsoft integrates cybersecurity into its processes, technologies, and the solution it provides. You can learn about the cybersecurity posture, Azure Native controls, Zero trust user access, and much more using the Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture.
Reasons to implement MCRA
Microsoft’s strong commitment to cybersecurity is among many reasons to use MCRA. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in security. It may be known for the solutions it provides; however, Microsoft invests a significant amount to build security into its core technology. Some of the more reasons to use MCRA as a reference architecture for your cybersecurity are given below:
Microsoft’s holistic security approach
Microsoft combines a three-fold security approach for its customers that includes platform, intelligence, and partners.
- A comprehensive platform enables to oversee all critical endpoints of the cloud and mobile devices to gain visibility into the security resources and provides more control over them.
- Vast intelligence enables to detect, protect, and respond to threats more effectively.
- Cybersecurity is not a problem to address alone. Microsoft’s broader partnerships make it easier to ensure customers’ needs and international regulations are met.
Leadership in cybersecurity
Microsoft takes pride in its leadership in cybersecurity as it collaborates with government and leading security organizations worldwide to share industry standards, provide guidance through its reference architecture and engage organizations to protect critical infrastructures.
Deep customer interaction
The Enterprise Cybersecurity Group (ECG) developed by Microsoft engages with customers across the globe to educate them through Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture, its security approach, and its services. Moreover, partnerships of ECG with a variety of different security-related teams help customers learn more about executive-level security and MCRA.
Benefits of MCRA for customers
Organizations looking for solutions to avoid the devastating impacts of cyber attacks need proven architecture to deploy cybersecurity in their systems and the cloud. The Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture is a proven approach to plan, implement, and protecting system networks and cloud workloads based on industry best practices. As a template solution, MCRA provides the standard to make better decisions, enable IIoT and maintain a security infrastructure. Customers may benefit from MCRA in the following ways.
● Maintain cloud security
In this era where most organizations depend on a hybrid approach, using on-premise data centers and cloud simultaneously, security remains a significant issue. Following the Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture can help you maintain robust cloud security. As a template solution, it provides insight into Microsoft’s security capabilities. Learning about them can help you enhance your own organizational security capabilities.
● Mitigate risks
MCRA includes Azure native controls and security operations to enable a rapid incident response. Organizations can benefit from this template to learn more about mitigating risks and how to respond in the event of a security incident.
● Implement zero trust user access
Implementation of the zero trust model enables organizations to continuously validate people, processes, and technologies to mitigate the risk of cyber attacks. MCRA provides visibility into the zero trust user access so that organizations can keep assets away from attackers. In addition, it provides a strategy to increase security for business assets as well as public and untrusted networks.
● Defend across attack chains
Internal and external risks are major threats to organizations. Insider threats are more dangerous than external threats as they occur due to an internal liability or weak point. 82% of breaches involve the human element. MCRA provides insight into insider risks and how they can lead to data leakage or potential sabotage. Organizations can use MCRA to enhance their insider risk management.
● Cost-effectiveness
A data breach can cost you millions. The average cost of a data breach in the United States amounted to $9.44 million in 2022. MCRA provides clear guidance on how to avoid cyber-attacks and data breaches. Using this template as a roadmap to enhance cybersecurity posture can significantly minimize data breaches, consequently reducing the cost spent to recover from a breach.
Takeaway!
As the risks of cyber-attacks increase, organizations must turn to a solution that can help them maintain their security capabilities. Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architecture not only offers visibility into its own security posture but also enables organizations to benefit from the template to create and maintain their cybersecurity architecture.

